Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=3SyRXJAAAAAJ&hl=en
(I) Artificial synthetic cells and protocells built upon chemistry, synthetic biology and micro-/nanomaterials for theranostic, biosensing, bioenergy conversion and life-of-origin researches.
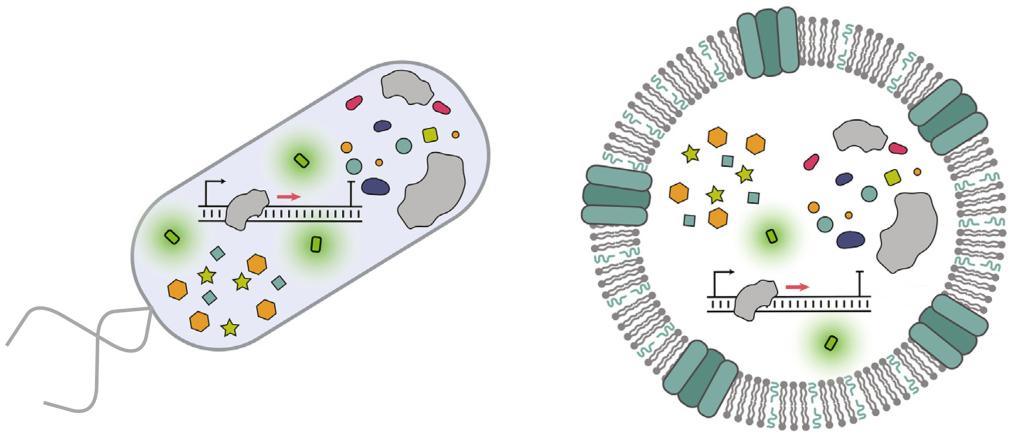
(1) Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, W.; Archibong, E.; Kahkoska, A. R.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Ligler, F. S.; Buse, J. B.; Gu, Z.* Synthetic beta cells for fusion-mediated dynamic insulin secretion. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 86-93.
(2) Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, P.; Zhang, J.; Tira, G.; Kim, Y. J.; Wu, Y. A.; Liu, Y.; Wen, J.; Rajh, T.; Niklas, J.; Poluektov, O. G.; Laible, P. D.; Rozhkova, E. A.* Semi-artificial Photosynthetic CO2 Reduction through Purple Membrane Re-engineering with Semiconductor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11811-11815.
(3) Chen, Z.; De Queiros Silveira, G.; Ma, X.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Y. A.; Barry, E.; Rajh, T.; Fry, H. C.; Laible, P. D.; Rozhkova, E. A.* Light-Gated Synthetic Protocells for Plasmon-Enhanced Chemiosmotic Gradient Generation and ATP Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4896-4900.
(4) Chen, Z.*; Wen, D.; Gu, Z.* Cargo-encapsulated cells for drug delivery. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 599-601.
(5) Han, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, D.; Chen, Z.*; Gu, Z.* Local and Targeted Delivery of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapeutics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2521-2533.
(6) Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Z.* Bioinspired and Biomimetic Nanomedicines. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1255-1264.
(7) Chen, Z.; Hu, Q.; Gu, Z.* Leveraging Engineering of Cells for Drug Delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 668-677.
(8) Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.*; Yang, H.*; Gu, Z.* Cellular transformers for targeted therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 114032.
(II) Inspired by the nature of metalloenzyme-catalyzed reactions, metal complex (artificial enzymes) or metal nanoparticles (bioorthogonal catalysts) can be synthesized and utilized as abiotic catalysts for deploying artificial chemistry in biological environments.

(1) Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Bian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Miao, Y.; Wen, D.; Wang, J.; Wan, G.; Zeng, Y.; Abdou, P.; Fang, J.; Li, S.; Sun, C.-J.; Gu, Z. Bioorthogonal catalytic patch. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 933-941. (Cover of the August Issue; highlighted by Matter and F1000 Faculty Opinions)
(2) Ouyang, D.; Yang, R.; Yao, Y.*; Jiang, F.; Song, S.; Yang, Y.; Ogunnaike, E. A.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.*; Yang, H.* In Situ PROTAC Synthesis Enabled by Pathologically Activated Bioorthogonal Catalysis for Precision Cancer Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c15945.
(3) Zeng, F.; Pan, Y.; Wu, M.; Lu, Q.; Qin, S.; Gao, Y.; Luan, X.; Chen, R.; He, G.; Wang, Y.; He, B.*; Chen, Z.*; Song, Y*. Self-Metallized Whole Cell Vaccines Prepared by Microfluidics for Bioorthogonally Catalyzed Antitumor Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2024, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c09871.
(4) Chen, Z.; Ji, H.; Liu, C.; Bing, W.; Wang, Z.; Qu, X.* A Multinuclear Metal Complex Based DNase-Mimetic Artificial Enzyme: Matrix Cleavage for Combating Bacterial Biofilms. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10732-10736.
(5) Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Qu, X.* Enzyme Mimicry for Combating Bacteria and Biofilms. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 789-799.
(6) Guo, Y.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, X.; He, W.; Song, S.; Shou, X.; Wu, M.; Wu, T.; Huang, T.; Ye, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.*; Yao, Y.*; Chen, Z.*; Yang, H. An enzyme-gated bioorthogonal catalytic nanoreactor for tumor-specific prodrug activation. Nano Res. 2025, 18, 94907134.
(III) The high spatiotemporal resolution of light makes optical nanomaterials promising for therapeutic/bioimaging studies, and developing optogenetic light delivery devices.
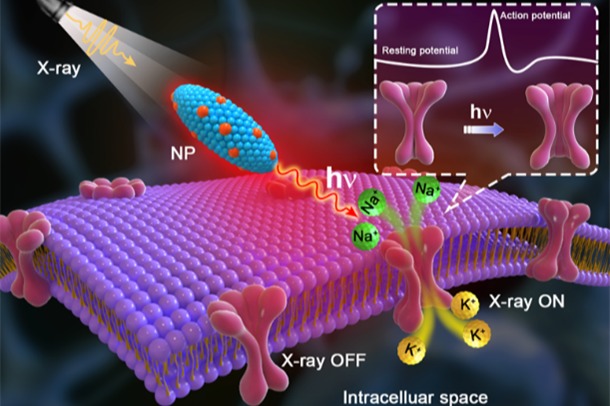
(1) Hong, Z.; Chen, Z.*; Chen, Q.*; Yang, H.* Advancing X-ray Luminescence for Imaging, Biosensing, and Theragnostics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 37-51.
(2) Chen, Z.; Tsytsarev, V.; Finfrock, Y. Z.; Antipova, O. A.; Cai, Z.; Arakawa, H.; Lischka, F. W.; Hooks, B. M.; Wilton, R.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Gaitan, B.; Tao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Erzurumlu, R. S.; Yang, H.; Rozhkova, E. A.* Wireless Optogenetic Modulation of Cortical Neurons Enabled by Radioluminescent Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5201-5208.
(3) Tang, X.; Chen, Z.*; Yang, H.* Near-infrared-II-activated photothermal nanotransducers for wireless neuronal stimulation. MedComm – Biomaterials and Applications 2022, 1, e15.
(4) Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Ju, E.; Zhou, L.; Ren, J.*; Qu, X.* A Multi-synergistic Platform for Sequential Irradiation-Activated High-Performance Apoptotic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 522-529.
(5) Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Ju, E.; Gao, N.; Zhou, L.; Ren, J.*; Qu, X*. Upconversion nanoprobes for efficiently in vitro imaging reactive oxygen species and in vivo diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials 2015, 39, 15-22.
(IV) Bioinspired microreactors made of Pickering emulsions, colloidal particle-stabilized droplets, or functional nanomaterial-integrated living cells, for biocatalytic conversion applications and beyond.
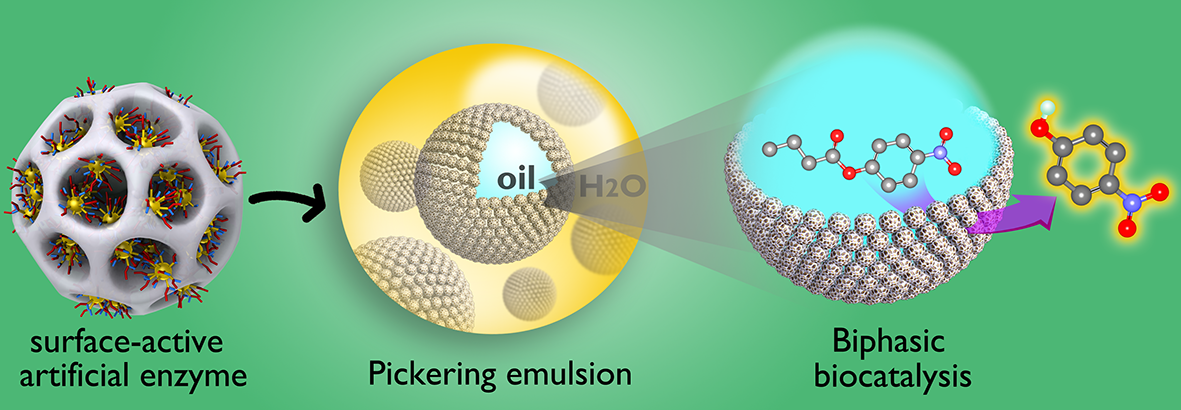
(1) Xu, X.; Zhou, M.; Wu, T.; Chen, Z.*; Yang, H.* Pickering emulsion-based biomimetic microreactors. Mater. Chem. Front. 2025, DOI: 10.1039/D5QM00079C.
(2) Xu, X.; Xie, W.; Wu, T.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Lian, H.; Chen, H.; Cheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, L.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.*; Binks, B. P.*; Yang, H.* Bacterial microcompartment-mimicking Pickering emulsion droplets for detoxification of chemical threats under sweet conditions. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 3039-3049.
(3) Chen, Z.; Rozhkova, E. A.* Intracellular gold nanoclusters boost energy conversion. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 880-881.
(4) Chen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Ju, E.; Ji, H.; Ren, J.;* Binks, B. P.*; Qu, X.* Design of Surface-Active Artificial Enzyme Particles to Stabilize Pickering Emulsions for High-Performance Biphasic Biocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1682-1688.
(5) Chen, Z.; Ji, H.; Zhao, C.; Ju, E.; Ren, J.*; Qu, X.* Individual Surface-Engineered Microorganisms as Robust Pickering Interfacial Biocatalysts for Resistance-Minimized Phase-Transfer Bioconversion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4904-4908.
(6) Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Bing, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Ren, J.*; Qu, X*. Light Controlled Reversible Inversion of Nanophosphor-Stabilized Pickering Emulsions for Biphasic Enantioselective Biocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7498-7504.
(V) The rich chemical, physical and biological functions of biomolecules, like DNA, protein, and polysaccharides, enabled us to develope advanced theranostic platforms for biomedical engineering applications.
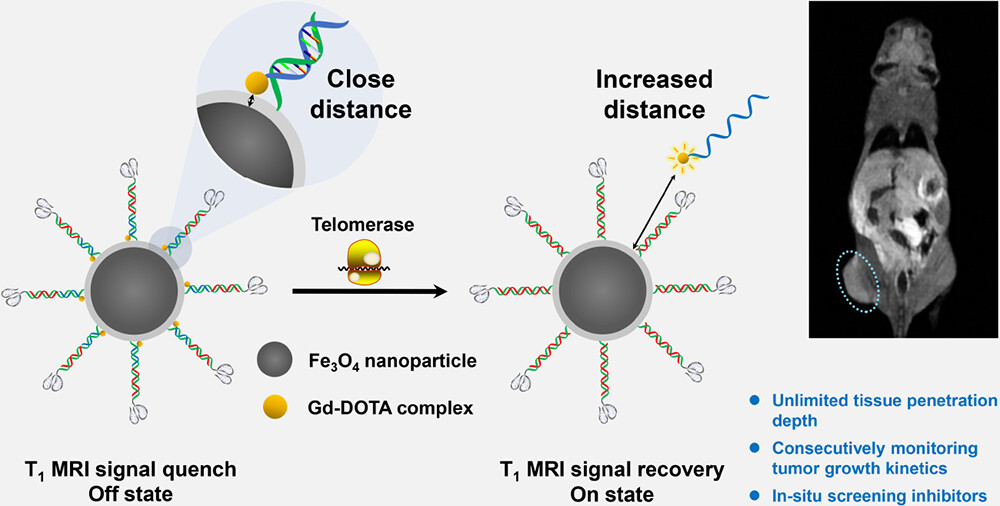
(1) Dai, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, G.; Song, S.; Chen, C.; Wu, T.; Xu, X.; Hao, C.; Bian, Y.; Rozhkova, E. A.*; Chen, Z.*; Yang, H.* A Telomerase-Activated Magnetic Resonance Imaging Probe for Consecutively Monitoring Tumor Growth Kinetics and In Situ Screening Inhibitors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 1108-1117.
(2) Song, S.; Wang, Q.; Xie, J.; Dai, J.; Ouyang, D.; Huang, G.; Guo, Y.; Chen, C.; Wu, M.; Huang, T.; Ruan, J.; Cheng, X.; Lin, X.; He, Y.*; Rozhkova, E. A.*; Chen, Z.*; Yang, H.* Dual-Responsive Turn-On T1 Imaging-Guided Mild Photothermia for Precise Apoptotic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023, 12, 2301437.
(3) Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Hao, C.; Xie, W.; Huang, T.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Q.; Huang, S.; Ye, Z.; Lin, X.; Chen, Z.*; Chen, Z.* Remodel the Perifollicular Microenvironment via Minoxidil-loaded Microneedle Patch and Cold Atmospheric Plasma for Treating Androgenetic Alopecia. Nano Res. 2024, DOI: 10.1007/s12274-024-6619-0.
(4) Song, S.; Wang, Q.; Xie, J.; Guo, Y.; He, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, B.; Chen, Z.; Lin, X.; He, Y.*; Tian, W.*; Chen, Z.* A DNA machine-based magnetic resonance imaging nanoprobe for in vivo microRNA detection. Talanta 2025, 281, 126867.
(5) Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Cao, F.; Ren, J.*; Qu, X.* DNA metallization: principles, methods, structures, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 4017-4072.